
Early Signs, Treatment Options, and Dietary Tips for Joint Health
Arthritis affects millions in the US, with symptoms often appearing in hands, shoulders, and other joints. Recognizing early signs and exploring treatments, including dietary choices, can improve quality of life.
Related Topics (Sponsored Ads)
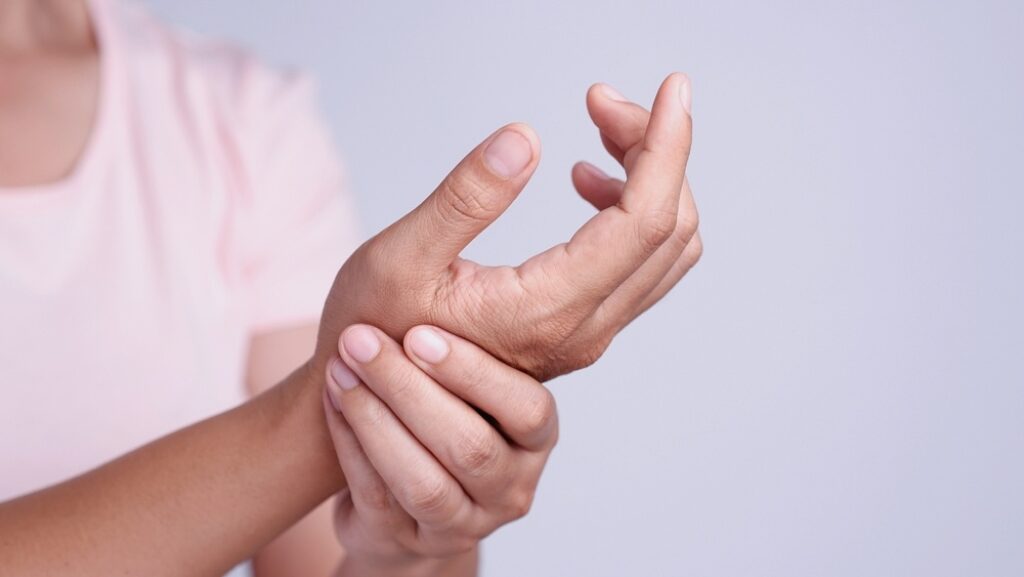
Recognizing the Early Signs of Arthritis
Identifying early signs of arthritis can lead to more effective management. In its initial stages, arthritis might manifest as subtle discomfort or stiffness. Here are some early symptoms to watch for:
- Pain and Stiffness: Joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the hands, shoulders, and knees, are common early symptoms. This discomfort is usually worse after inactivity or in the morning.
- Swelling and Redness: Inflammation can cause joints to swell and become red, making them tender to the touch.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving joints smoothly or a decreased range of motion can be early indicators of arthritis.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or experiencing a general sense of malaise can accompany the onset of arthritis.
- Warmth in the Joints: A feeling of warmth around the affected joints can be a sign of inflammation.
Recognizing these signs early and seeking medical advice can prevent further joint damage and help maintain mobility.
Understanding Different Types of Arthritis
Arthritis encompasses over 100 different types. Here, we focus on two common types: osteoarthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common form of arthritis, often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time. Osteoarthritis commonly affects joints in your hands, knees, hips, and spine.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis affects some people who have psoriasis, a condition that features red patches of skin topped with silvery scales. Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are the primary symptoms, which can affect any part of your body, including your fingers and spine.
Understanding the type of arthritis you have is crucial as it influences the treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Arthritis
Managing arthritis involves a combination of treatments tailored to reduce symptoms and improve joint function. Here are some common treatment strategies:
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics can help manage pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are also used for inflammatory types like rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can improve mobility and strengthen the muscles around the joints, providing better support.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options like joint repair, fusion, or replacement may be considered.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and using assistive devices can alleviate stress on the joints and improve quality of life.
It’s essential for individuals to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific condition and lifestyle.
Dietary Tips for Managing Arthritis
Diet plays a significant role in managing arthritis. Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, while others can help reduce it. Here’s a list of foods to eat and avoid:
Foods to Eat:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and mackerel, omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants, they help reduce inflammation. Berries, spinach, and broccoli are excellent choices.
- Whole Grains: Foods like oatmeal, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread can reduce inflammation markers.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are beneficial due to their healthy fats and protein content.
Foods to Avoid:
- Processed Foods: High in trans fats and sugar, they can increase inflammation.
- Red Meat: Contains high levels of saturated fats that can worsen inflammation.
- Dairy Products: For some individuals, dairy can trigger inflammation. It’s worth monitoring to see if it affects your symptoms.
- Refined Carbs: Such as white bread and pastries, which can spike blood sugar levels and increase inflammation.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet while avoiding those that exacerbate symptoms can significantly impact arthritis management.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to manage effectively. By recognizing the early signs, understanding the type of arthritis, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can lead a more comfortable and active life. Additionally, dietary modifications play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease. By making informed choices and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can navigate the challenges of arthritis more effectively and maintain their quality of life.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.




