
Common Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
When it comes to your physical health, one of your best friends is your body itself. Most diseases and bad health conditions have tell-tale warning signs, letting you know there is a problem. However, you have to know what these symptoms are. This is especially true for heart related medical problems.
Related Topics (Sponsored Ads):
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a prevalent cardiovascular condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. It occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This article explores the common symptoms of CAD, along with the associated risk factors and available treatments.
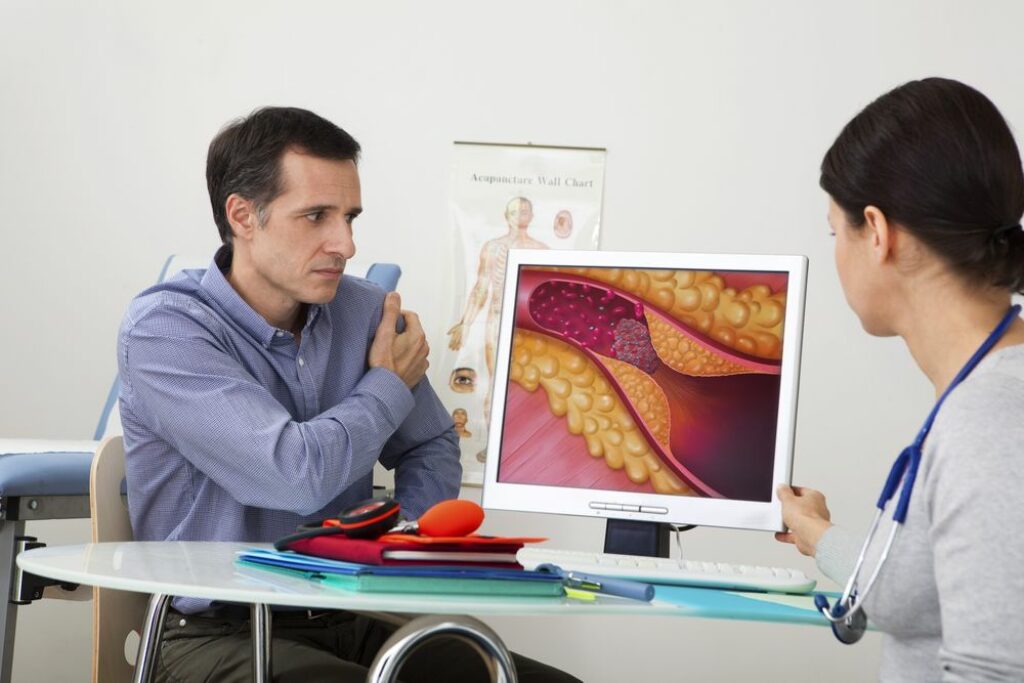
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
– Chest Discomfort: The most common symptom of CAD is angina, a type of chest discomfort or pain. It is often described as a pressure, squeezing, or tightness in the chest, which may radiate to the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back. Angina typically occurs during physical exertion or emotional stress and subsides with rest.
– Shortness of Breath: Many CAD patients experience shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying flat. This occurs because reduced blood flow to the heart impairs its ability to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body, leading to breathlessness.
– Fatigue and Weakness: CAD can cause persistent fatigue and weakness due to the heart’s reduced ability to pump blood effectively. The inadequate blood supply to the heart muscles deprives them of the required oxygen, leading to feelings of tiredness and weakness.
– Heart Palpitations: Some individuals with CAD may experience irregular heartbeats or palpitations. These sensations may feel like a racing, fluttering, or pounding heart. Palpitations can be accompanied by dizziness or lightheadedness.
– Indigestion or Nausea: CAD-related chest discomfort may mimic symptoms of indigestion or heartburn. Some individuals may experience nausea, stomach pain, or a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
– Sweating: Profuse sweating, especially without apparent cause, can be a symptom of CAD. The body reacts to reduced blood flow by releasing stress hormones, which can trigger excessive sweating.
Other Symptoms
CAD can manifest in less common ways, such as jaw pain, toothache, arm or shoulder pain, or even flu-like symptoms. Women may experience atypical symptoms, including fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Risk Factors
– Age and Gender: The risk of developing CAD increases with age, and men are generally at a higher risk than premenopausal women. However, the risk in women increases after menopause, and eventually, the gender gap narrows.
– High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a significant risk factor for CAD. Elevated blood pressure damages the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
– High Cholesterol Levels: Increased levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, known as “bad” cholesterol, contribute to plaque formation in the arteries. Conversely, higher levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol, help protect against CAD.
– Smoking: Cigarette smoking damages the blood vessels and accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of CAD.
– Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Being overweight or obese and leading a sedentary lifestyle are associated with an increased risk of CAD. Lack of regular physical activity contributes to weight gain and adversely affects heart health.
– Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to developing CAD. The combination of high blood sugar levels and other diabetic complications accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis.
– Family History and Genetics: A family history of CAD increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Genetic factors play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to CAD.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
CAD diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and various tests. These tests may include an electrocardiogram (ECG), stress test, echocardiogram, coronary angiogram, or cardiac catheterization.
Treatment Options
– Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial in managing CAD. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, smoking cessation, weight management, and stress reduction techniques.
– Medications: Various drugs are prescribed to control symptoms, prevent complications, and manage risk factors associated with CAD. These may include antiplatelet agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, beta-blockers, nitroglycerin, or angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
– Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases of severe CAD, angioplasty with stent placement may be performed. This procedure involves widening the blocked artery using a balloon catheter and placing a stent to keep the artery open.
– Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): CABG is a surgical procedure that involves bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries using blood vessels from other parts of the body. It is typically considered when multiple or complex blockages are present.
Final Thoughts
CAD is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. With appropriate lifestyle changes, medications, and interventions, individuals with CAD can lead fulfilling lives and reduce the risk of complications.
It is essential that you consult with an appropriate health care professional as soon as possible if you think you have CAD.




