
What is Melasma and How Can it Be Treated?
People usually associate skin conditions with serious diseases like cancer or various unpleasant symptoms, such as pain, flaking, redness, itchiness and irritation. But there is a type that is both painless and physically harmless, known as Melasma.
Related Topics (Sponsored Ads):
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the face caused by excessive amounts of melanin (pigment) in the individual’s skin. It primarily affects women, especially those with darker skin tones. While melasma is harmless and does not cause any physical discomfort, it can significantly impact a person’s self-esteem and confidence. By following a comprehensive treatment approach, individuals with melasma can gain more control over their skin and improve their self-esteem.
This article will explore what melasma is, its causes and risk factors, as well as non-medical treatments, medical treatments, and prevention tips to effectively manage and reduce the appearance of melasma.
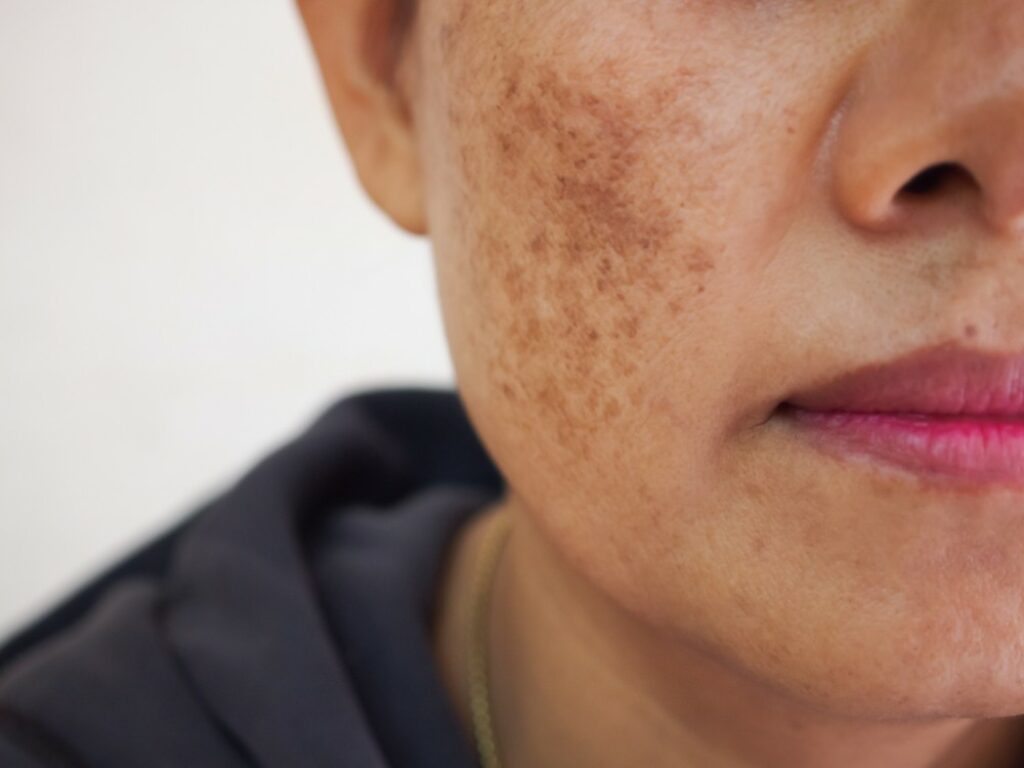
What is Melasma?
Melasma, also known as “chloasma” or “pregnancy mask,” is a skin condition that causes brown or grayish-brown patches to appear on the face. These patches typically occur on the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and upper lip. It is more prevalent in women, especially during pregnancy or when taking hormonal contraceptives. However, men can also develop melasma, albeit less frequently. It is believed that melasma is primarily caused by hormonal changes and sun exposure.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development. Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or while taking hormonal medications, play a significant role in triggering melasma. Sun exposure is another major factor, as ultraviolet (UV) rays can stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Other risk factors include a family history of melasma, a history of thyroid dysfunction, and certain medications that make the skin more prone to pigmentation.
Non-Medical Treatments
While there is no cure for melasma as of yet, several non-medical treatments can help manage and reduce its appearance. These treatments focus on minimizing pigmentation and protecting the skin from further damage. Some effective non-medical treatments include:
-Sun Protection: Wearing sunscreen with a high SPF (sun protection factor) daily and reapplying every two hours is crucial in preventing melasma from worsening. Additionally, wearing wide-brimmed hats and using umbrellas can provide extra protection against the sun’s harmful rays.
-Cosmetics: The use of color-correcting makeup and concealers can help camouflage melasma patches and even out skin tone. Look for products specifically designed to address hyperpigmentation.
-Chemical Peels: Chemical peels containing ingredients like glycolic acid or trichloroacetic acid can help exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of melasma. Regular peels, performed by a dermatologist, can lead to significant improvement over time.
-Topical Creams: Over-the-counter creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or retinoids can help fade melasma patches. However, it’s important to consult with a dermatologist before using any topical creams, as they may have side effects and require proper application.
Medical Treatments
In cases where non-medical treatments do not provide satisfactory results, dermatologists may recommend medical treatments to manage melasma. These treatments are generally more potent and should be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Some medical treatments for melasma include:
-Prescription Creams: Dermatologists may prescribe stronger creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, corticosteroids, or tretinoin to fade melasma patches. These creams are typically used for a limited duration due to potential side effects.
-Laser Therapy: Laser treatments, such as fractional laser therapy or intense pulsed light (IPL), can target and break up excess melanin in the skin, reducing the appearance of melasma. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
-Chemical Peels: Dermatologists can perform stronger chemical peels that penetrate deeper into the skin to target melasma. These peels may have a longer recovery time but can yield significant improvements.
-Microdermabrasion: This procedure involves exfoliating the outer layer of the skin to remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of melasma. It is a non-invasive treatment option that may require multiple sessions.
Prevention Tips
Prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to melasma. By adopting certain lifestyle habits and taking precautions, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition or prevent it from worsening.
The first thing you need to do is protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays by wearing sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses. Seek shade and avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours. Additionally, if you are prone to melasma due to hormonal changes, consult with your healthcare provider about potential alternatives to hormonal medications or contraceptives.
Practice gentle skincare. Use gentle cleansers and avoid harsh scrubs or abrasive treatments that can irritate the skin and worsen melasma. It’s also very helpful to identify and avoid triggers that may exacerbate your melasma, such as certain skincare products, hot showers, or excessive heat exposure.
Natural Remedies
While natural remedies may not provide the same level of effectiveness as medical treatments, they can be used in conjunction with other treatments to support the management of melasma. For instance, diluted apple cider vinegar can be applied topically to help lighten melasma patches. It is important to perform a patch test first and discontinue use if any irritation occurs. You can also try applying fresh aloe vera gel to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and potentially reduce pigmentation as well.
Believe it or not, vitamin C is beneficial for more than your immune health. By incorporating vitamin C-rich foods or serums into your skincare routine, this may help brighten the skin and improve melasma appearance over time. Last but not least, some studies suggest that licorice extract may have skin-lightening properties. It can be applied topically or found in certain skincare products.




